INKAS® Develops Oil-Containing Concrete For Environmental Remediation
INKAS® R&D team is proud to announce that it has developed and tested an oil-containing concrete for the cementation of organic liquids, which can aid in environmental remediation. This innovative method makes it possible to solidify radioactive organic liquids for safe long-term storage and incorporate oil-containing sands into structural concrete.
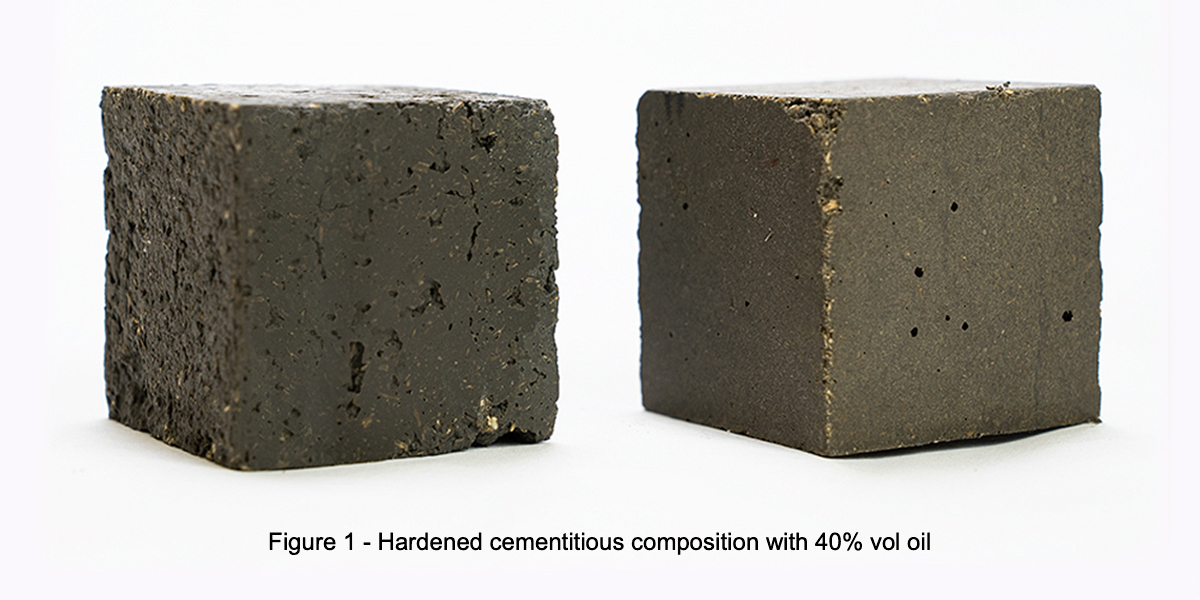
At the request of Oak Ridge National Laboratory, INKAS® R&D designed a special cementitious composition that is capable of producing concrete containing up to 40-50% oil by volume for the purposes of solidifying radioactive organic liquids to meet the requirements of the International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA).
The volume of radioactive organic liquids that have to be treated, is usually not more than a few cubic meters per year at one site, and thus despite its usefulness, this innovative cementitious composition does not have a large-scale application in this area.
During this research, INKAS® R&D team was able to demonstrate additional potential applications for this method, such as using oil-contaminated sand “as is” instead of natural fine aggregates for concrete production.
Crude oil spillage severely impacts the environment and affects the physical and chemical properties of the surrounding soil. Due to the substantial cost of cleanup efforts and disposal of oil-contaminated sand, mixing it instead with cement and using it in construction is a feasible alternative that results in a more affordable remediation method.
One of the most promising applications for this innovative method can be seen in Canada, with the ability to reduce the environmental impact of the oil sands tailings – which provide an important resource to Canada and the global market.
Oil Sands tailings are a mixture of water, sand, fine silts, clay, residual bitumen and lighter hydrocarbons, inorganic salts, and water-soluble organic compounds. With virtually unlimited resources at of the Oil Sands, INKAS® innovative cementitious composition is well-positioned as an effective solution for turning the oil sand tailings into structural concrete.
An example of the results of this method are demonstrated in Figure 1, which shows samples of hardened cementitious composition made for Oak Ridge National Laboratory, which contains 40% oil by volume.
INKAS® R&D team continues to explore applications and test this new method on various environmental remediation projects. The results thus far show great promise for minimizing human impact on the planet.
To learn more about other research completed by INKAS® R&D team, click here and here.
Comments are closed.